Advantages and Disadvantages of Oil-Immersed Test Transformers Oil-immersed test transformers are extensively utilized in power systems, industrial, mining enterprises, and various other sectors.
Within this category, there are different types such as gas-filled test transformers and dry-type test transformers. Let's explore the pros and cons of oil-immersed transformers.
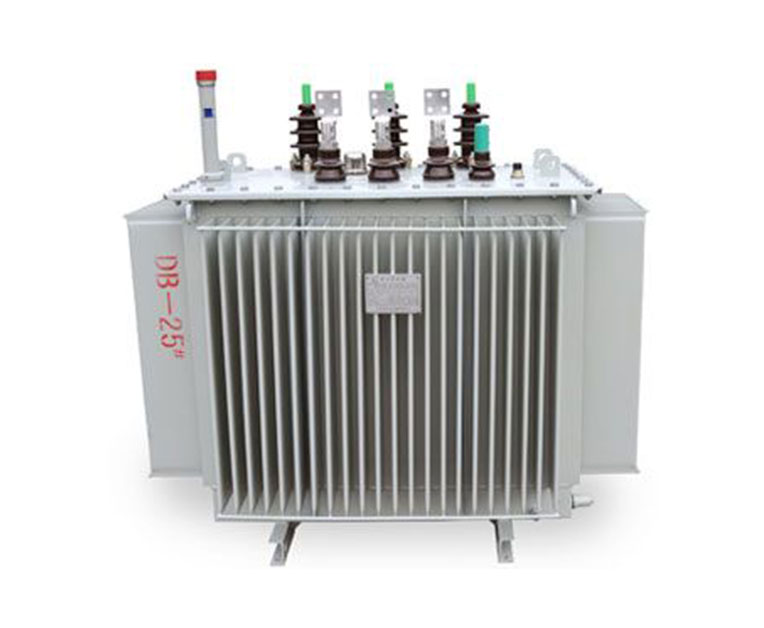

In comparison to dry-type and gas-filled test transformers, oil-immersed test transformers have the same internal windings but differ in the insulation material or medium used. Dry-type transformers utilize epoxy resin insulation, offering the advantage of being lightweight. However, they have limitations in voltage, with a maximum capacity of only 120kV, and are susceptible to fracturing upon impact. Gas-filled transformers, on the other hand, use SF6 gas insulation, providing high accuracy, high voltage capacity, lightweight construction, and a relatively higher price point. These transformers are commonly employed as standard voltage sources by metrology and testing institutions.
Oil-immersed test transformers utilize oil as the insulation medium, featuring high voltage capacity, large capacity, a sturdy metal casing, and a durable outer covering. They are much more cost-effective than dry-type and gas-filled transformers of equivalent capacity. Additionally, maintenance of oil-immersed transformers is both affordable and efficient. In case of a fault in the cable package, the process involves simply unscrewing the casing screws, draining the insulation oil, replacing the cable package, and refilling with fresh oil. When it comes to inspecting the transformers, oil-immersed test transformers offer greater convenience and speed compared to dry-type and gas-filled variants.